
Automating EBS Snapshot Deletion with AWS Lambda by EC2 Termination
Introduction
Hello, Hemanth from the Alliance Department here. In this blog, I'll walk you through the process of setting up an AWS Lambda function to automatically delete an EBS snapshot when an EC2 instance is terminated.
AWS
Is a secure cloud service platform that offers compute power, database storage, content delivery, network, and other functionality to help businesses scale and grow. It is one of the first cloud vendors to start services in the year 2006. It offers all the 3 service models namely IAAS, PAAS, and SAAS. Some of the notable domains in AWS are Compute, Migration, Storage, Network and Content Delivery, Management Tools, Database, Messaging, Security and Identity Compliance, and many more.
AWS Lambda
A serverless compute service which runs code as a reply to events and automatically takes care of the bottom resources. It runs code on high availability compute infrastructure and performs all the administration of the compute resources. A few examples are HTTP requests via Amazon API Gateway, changes to objects in S3, and many others.
EC2
It is a service offered by Amazon Web Services for cloud computing (AWS). By offering scalable cloud computing power through EC2, users can rent virtual computers on which to execute their own apps. When managing and scaling applications in the cloud, EC2 offers a flexible, affordable, and simple solution.
EBS
Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS) is a high-performance block storage service designed for use with EC2 instances. EBS volumes are automatically replicated within their Availability Zone to protect you from component failure, offering durability, availability, and reliability. EBS snapshots provide a way to back up the data stored on your EBS volumes.
Demo
Open the AWS Management Console and search for EC2. Click on Launch Instance.
Provide a name for your EC2 instance, leave other settings as default, and click Launch Instance.
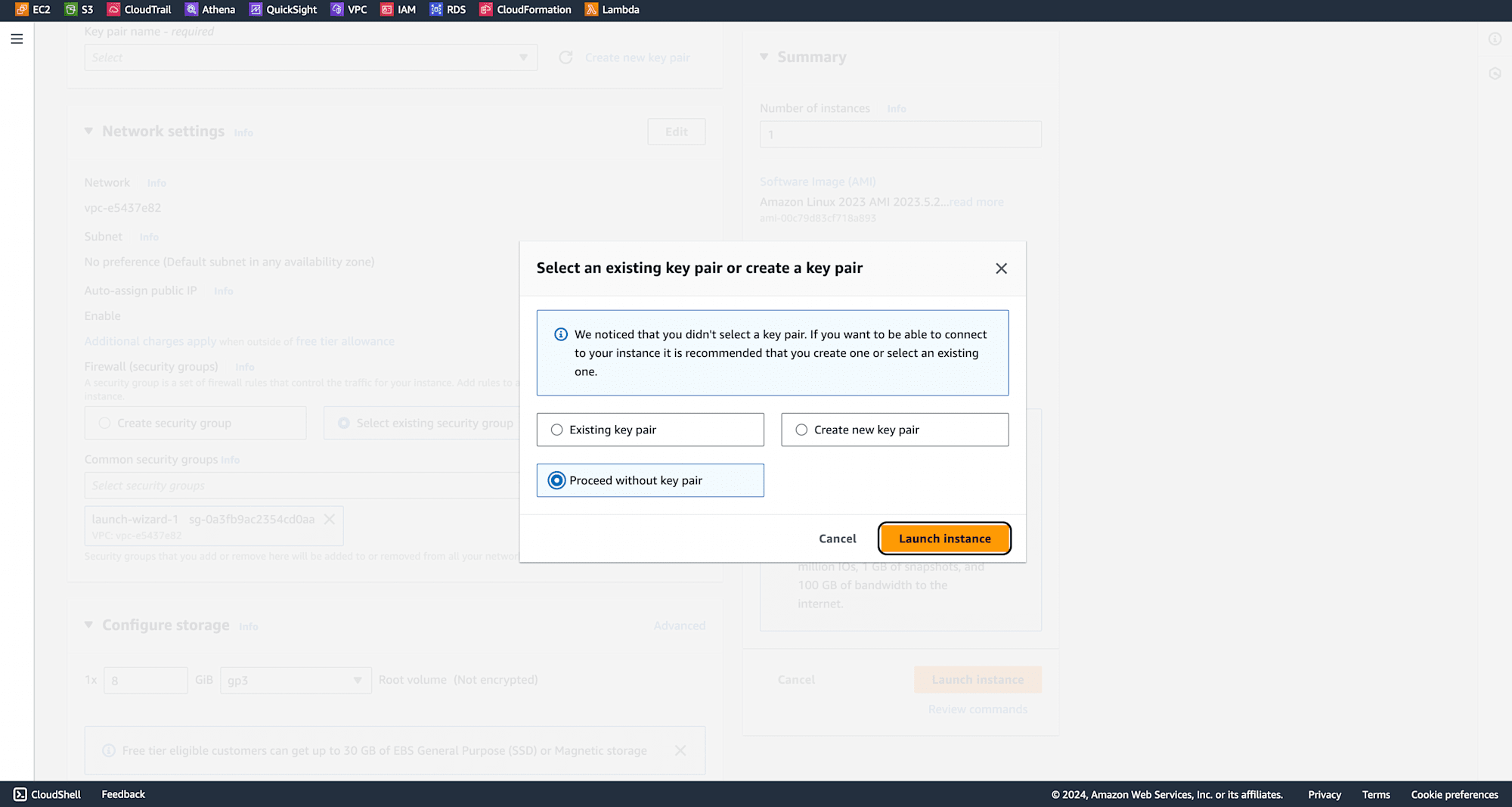
Select Proceed without a key pair and click Launch Instance. Note: You can launch any kind of instance and even with keypair.
EC2 instance is now launched, and an EBS volume is automatically created.
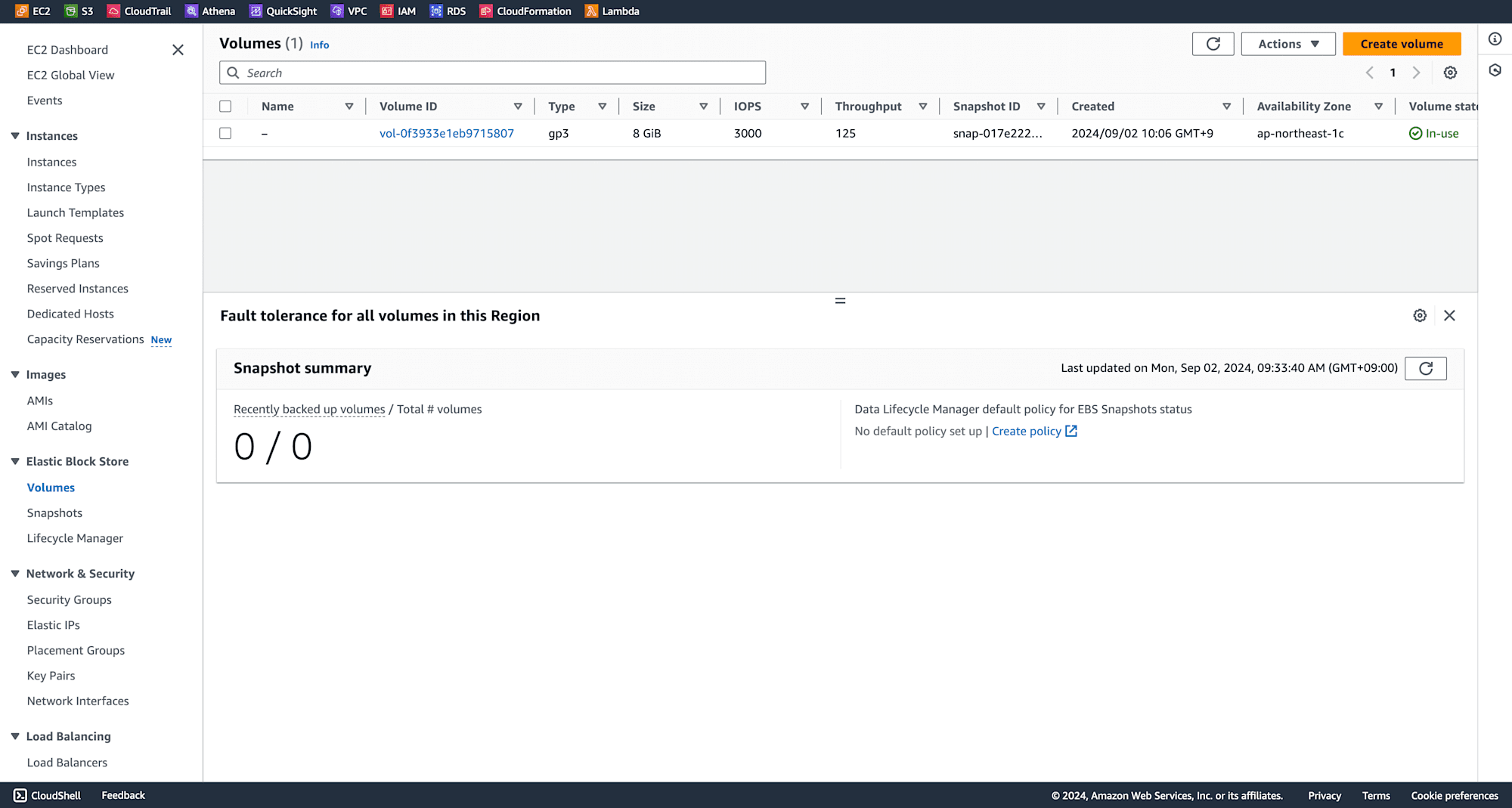
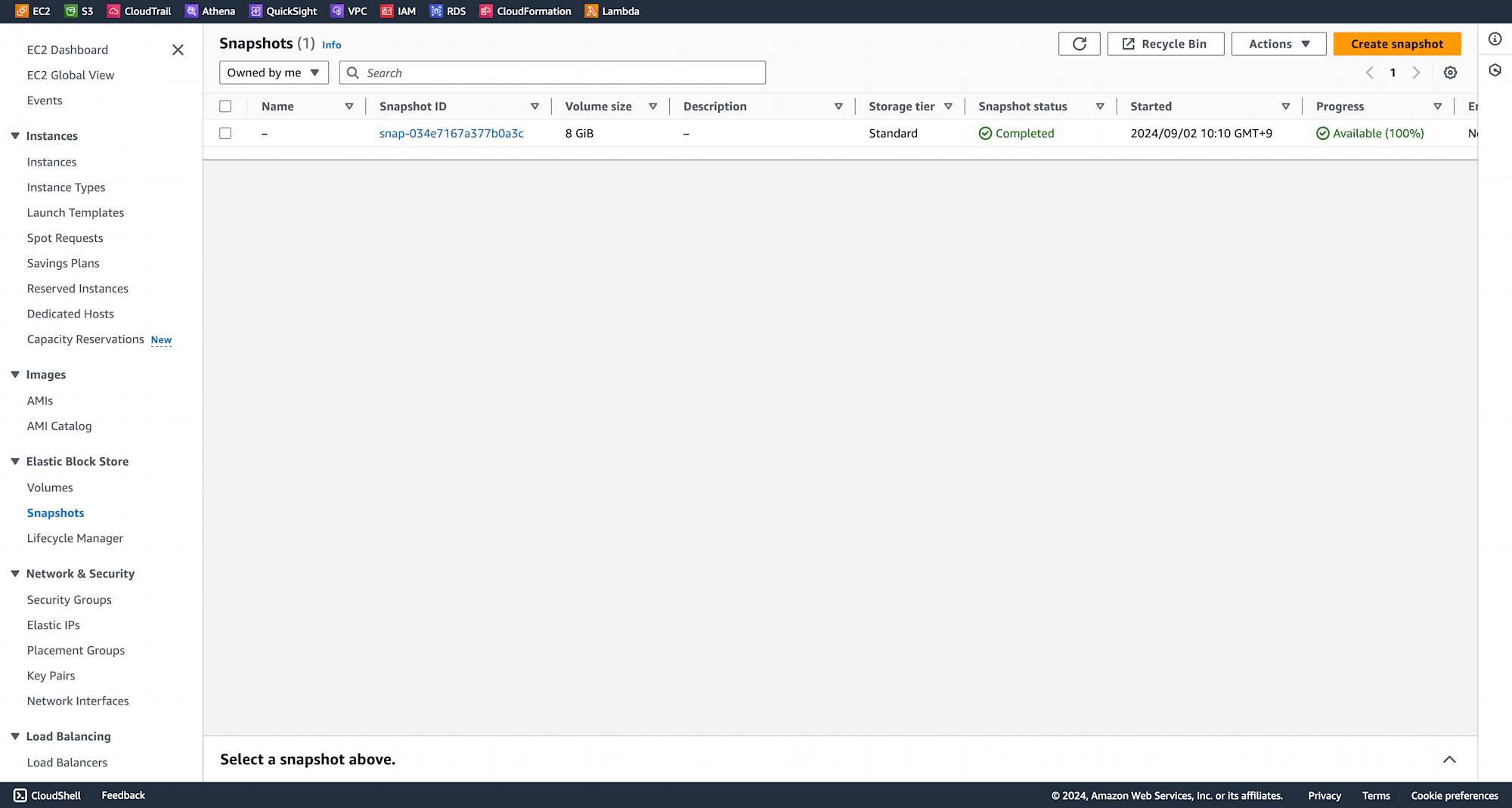
Navigate to Snapshots and click on Create Snapshot.
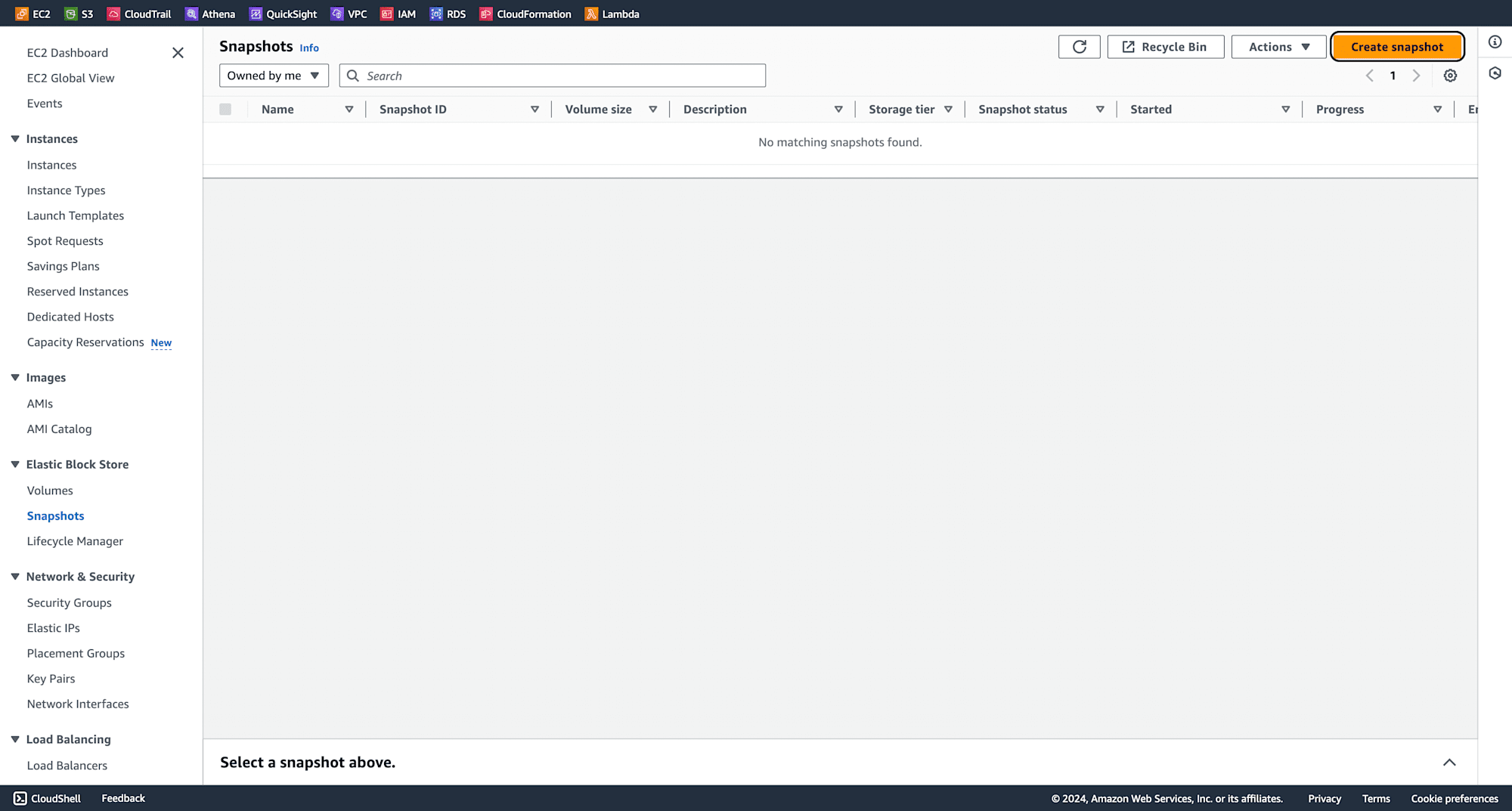
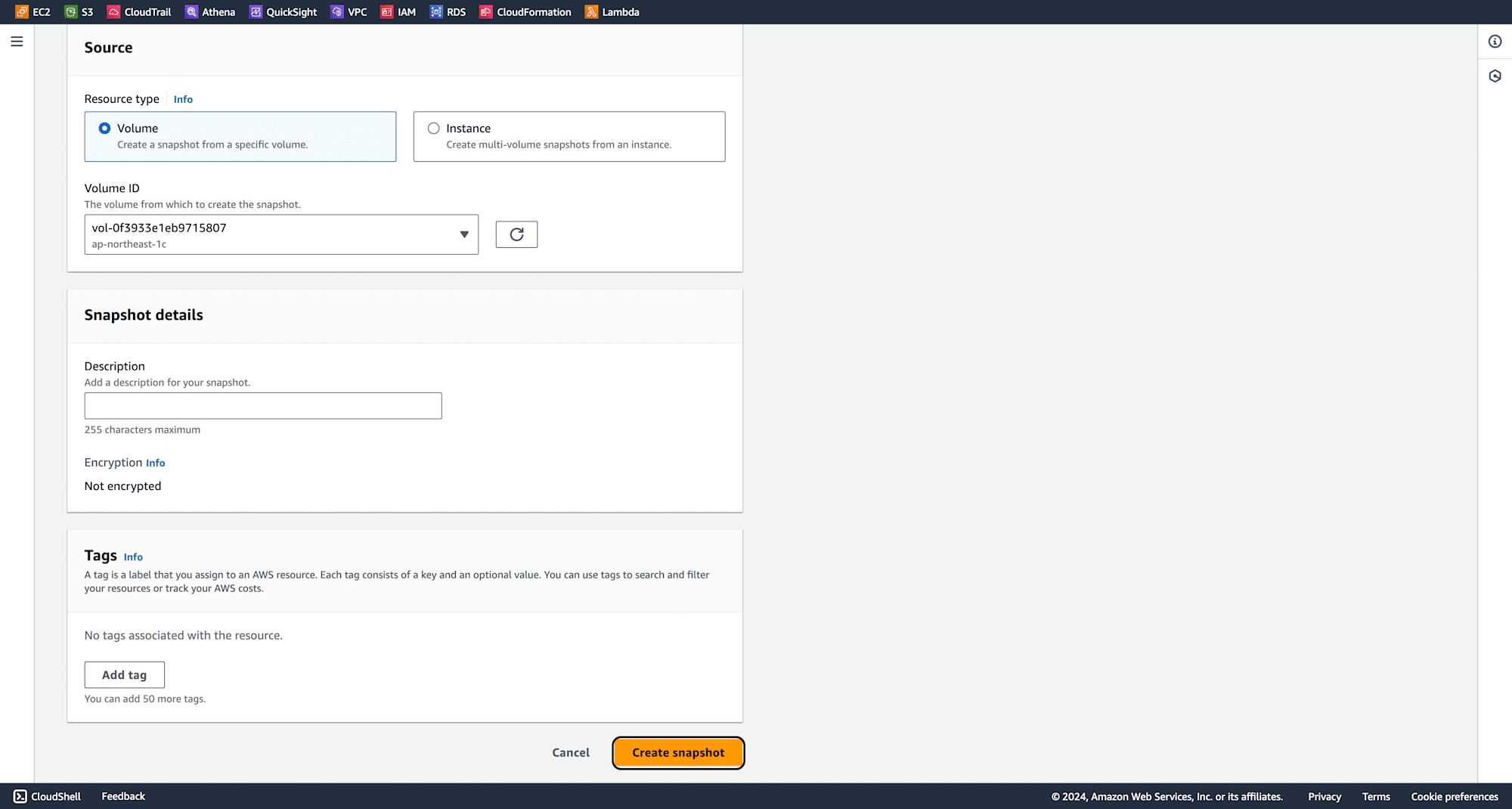
Select the volume created earlier and click on Create Snapshot.
In the AWS Management Console, search for Lambda and click on Create Function.
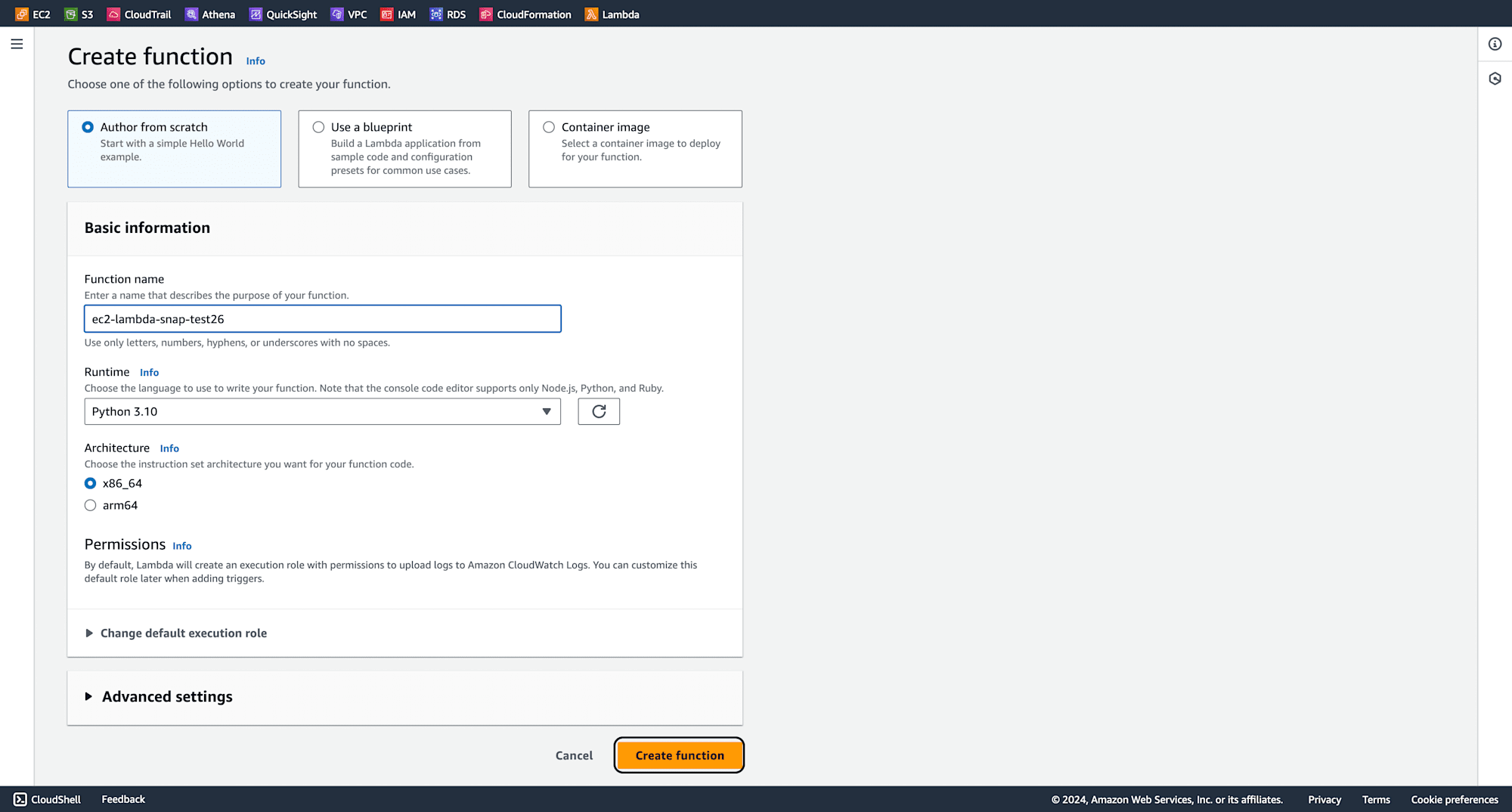
Give your function a name, select the Python runtime, leave other settings as default, and click Create Function.
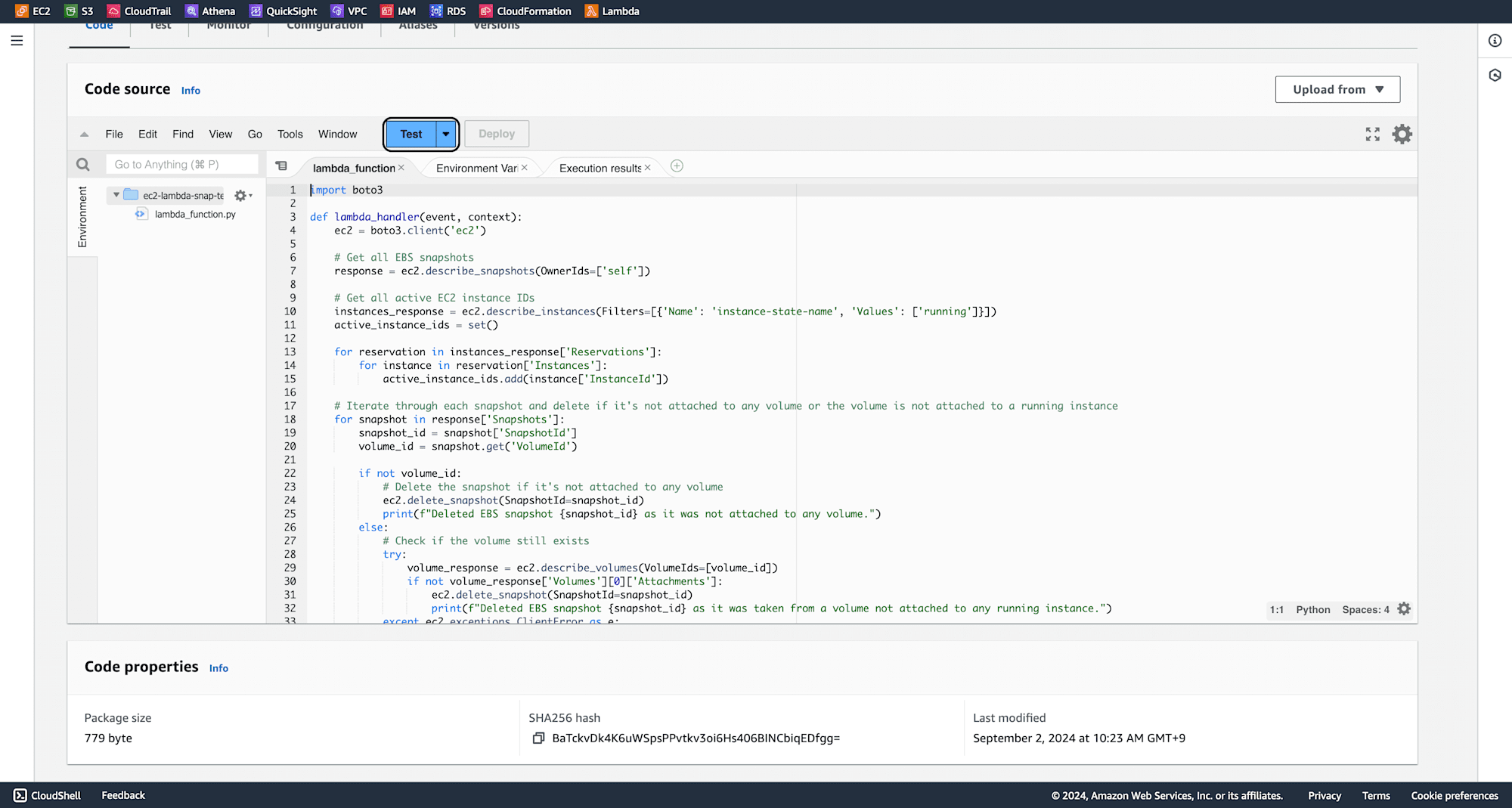
After the function is created, write the following code in the code editor:
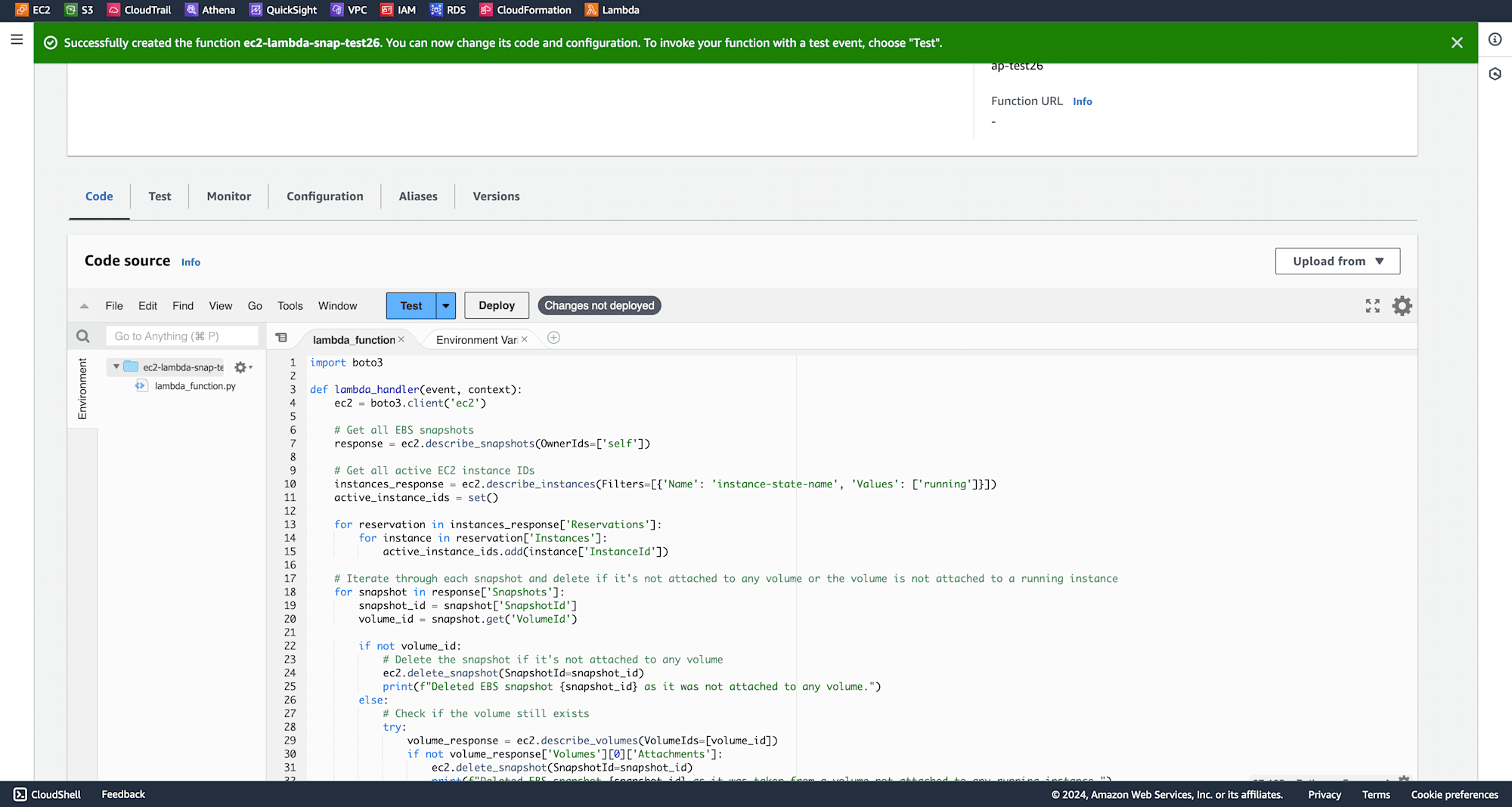
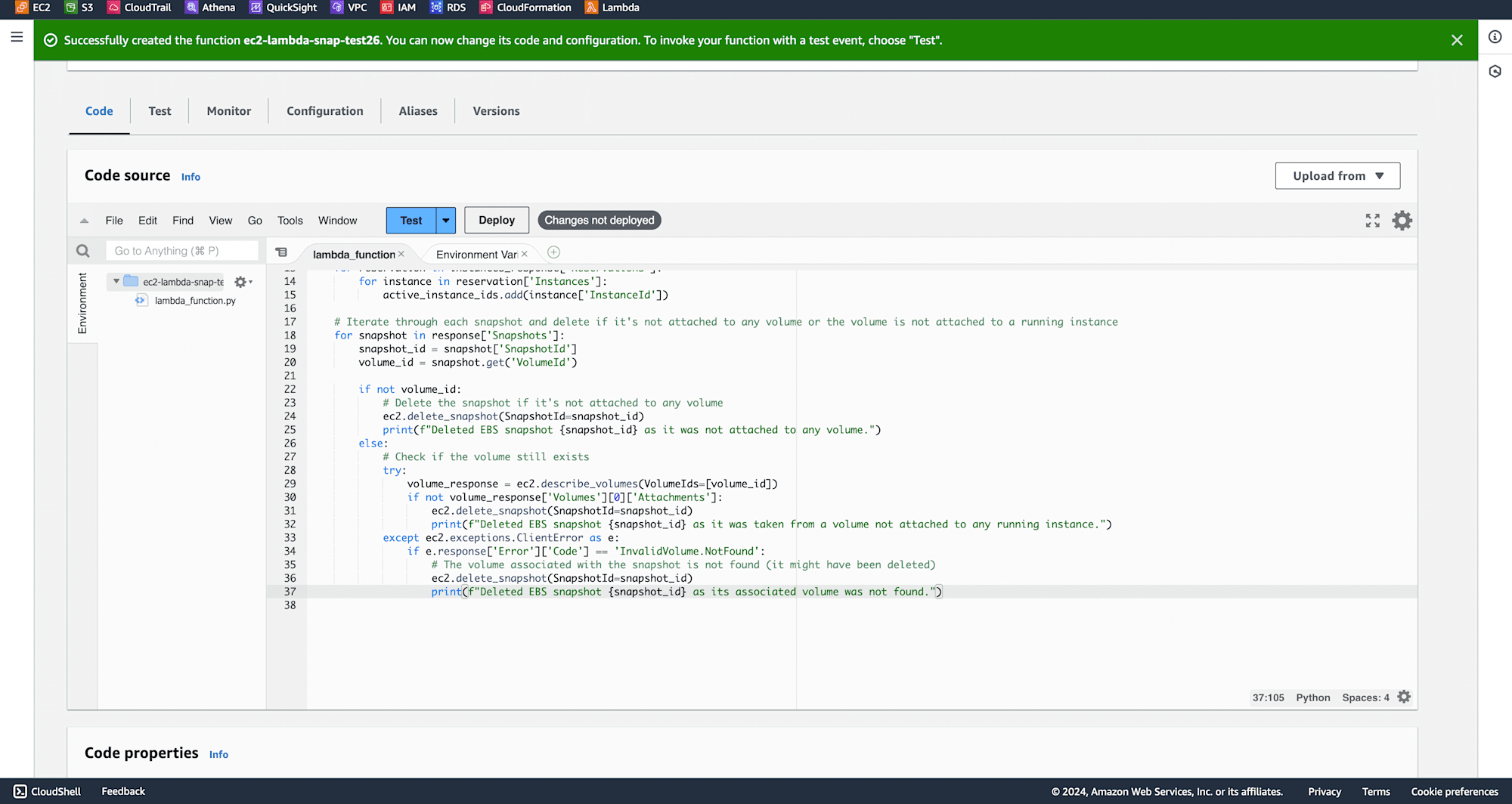
Under Configuration, select general configuration and click on Edit.
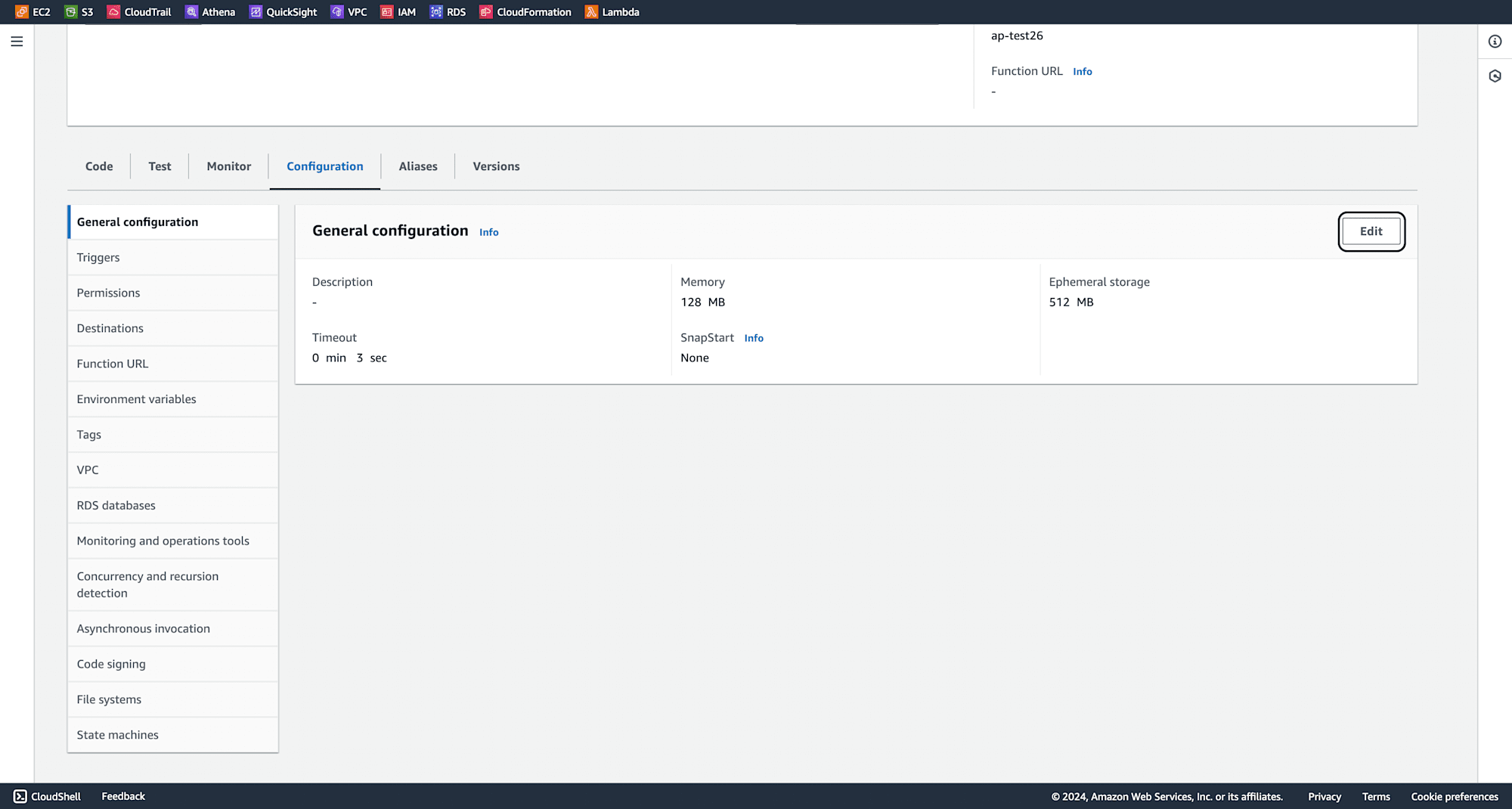
change the timeout to 10 seconds, then click Save.
Go to the Permissions tab and click on the role associated with your Lambda function.
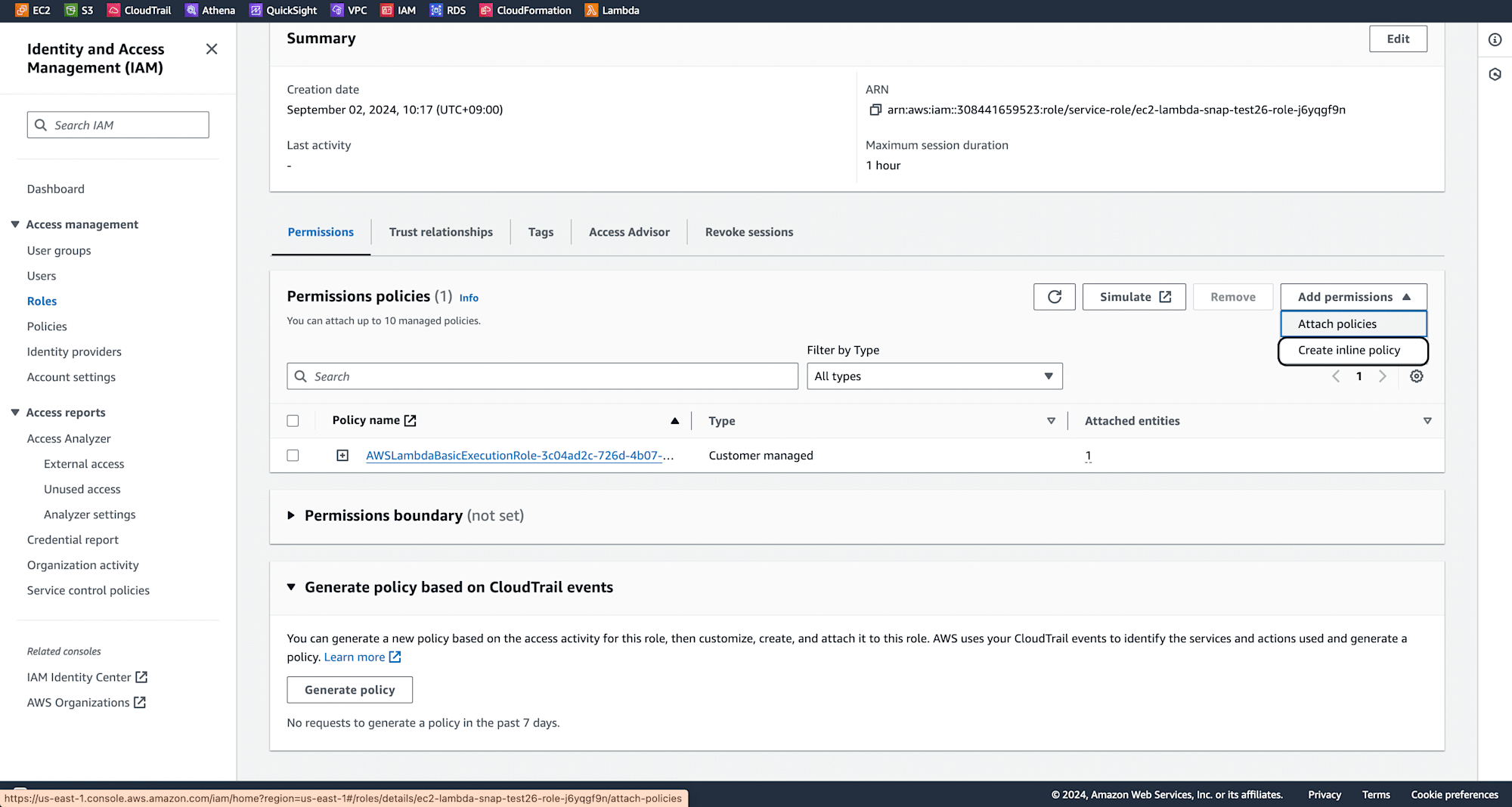
Click on Add Permissions and select Create Inline Policy.
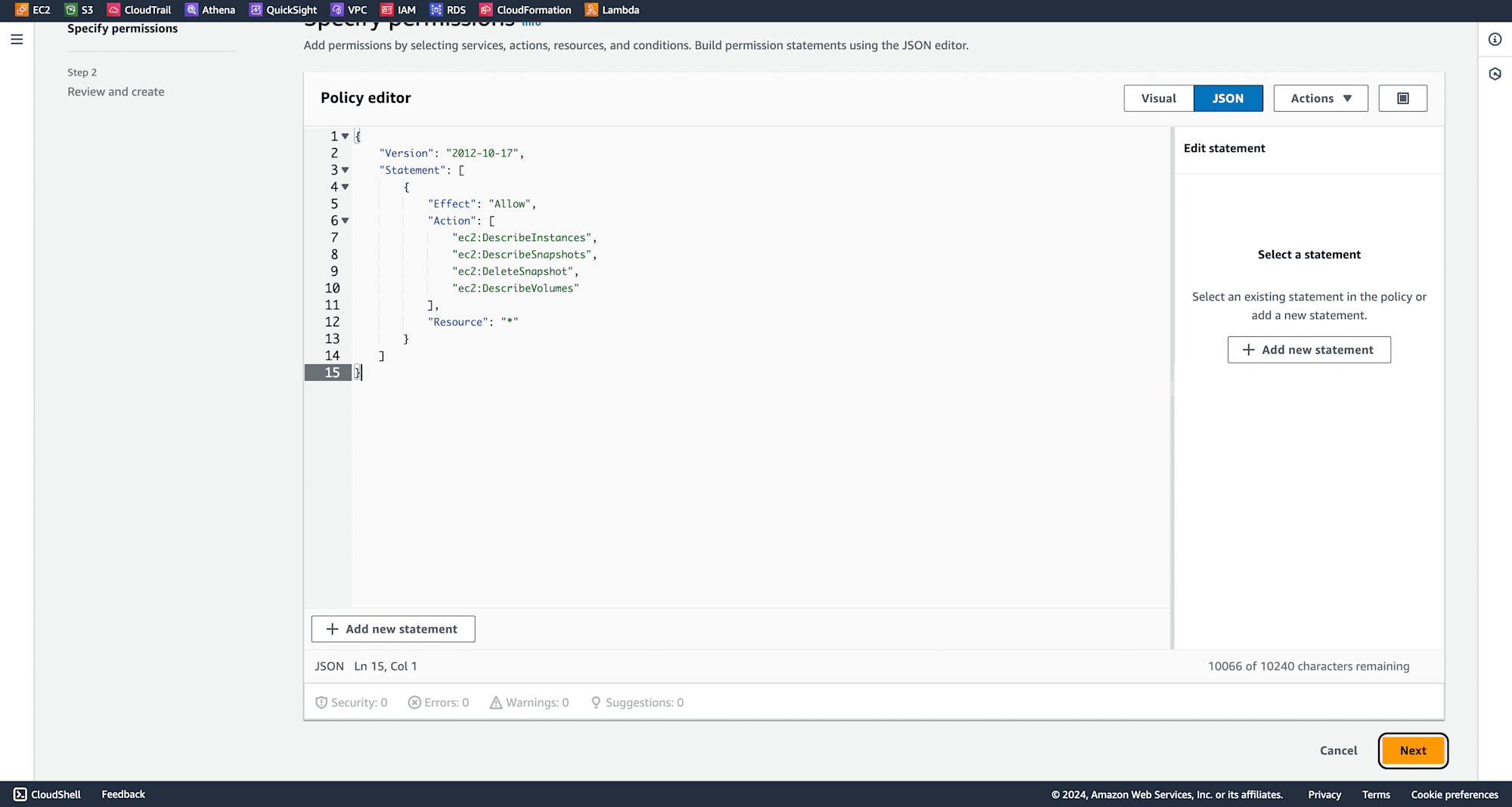
Choose the JSON tab and paste the following policy:
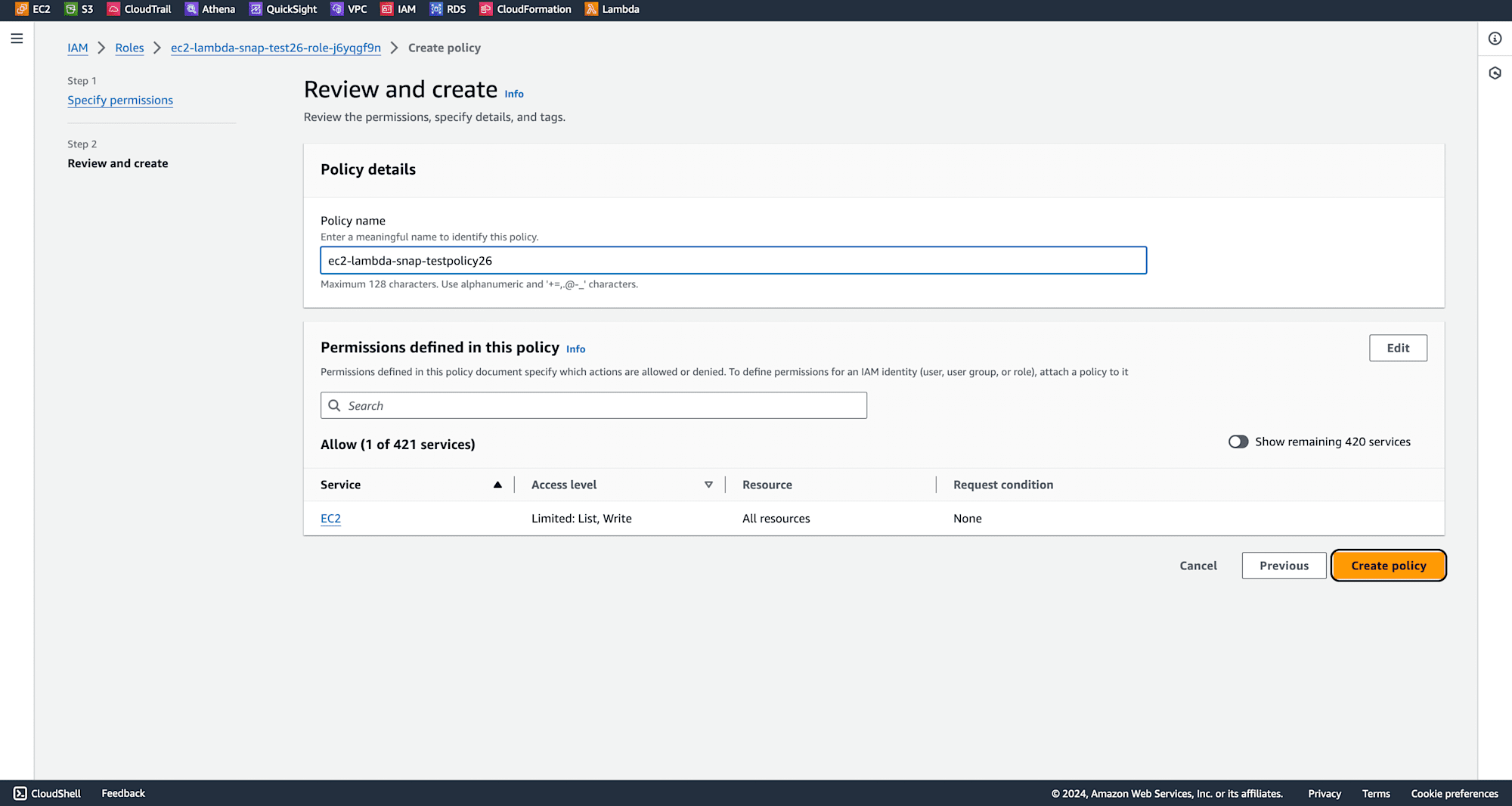
Name your policy and click on Create Policy.
Go back to your Lambda function and click on Deploy. Click on Test to run your function.
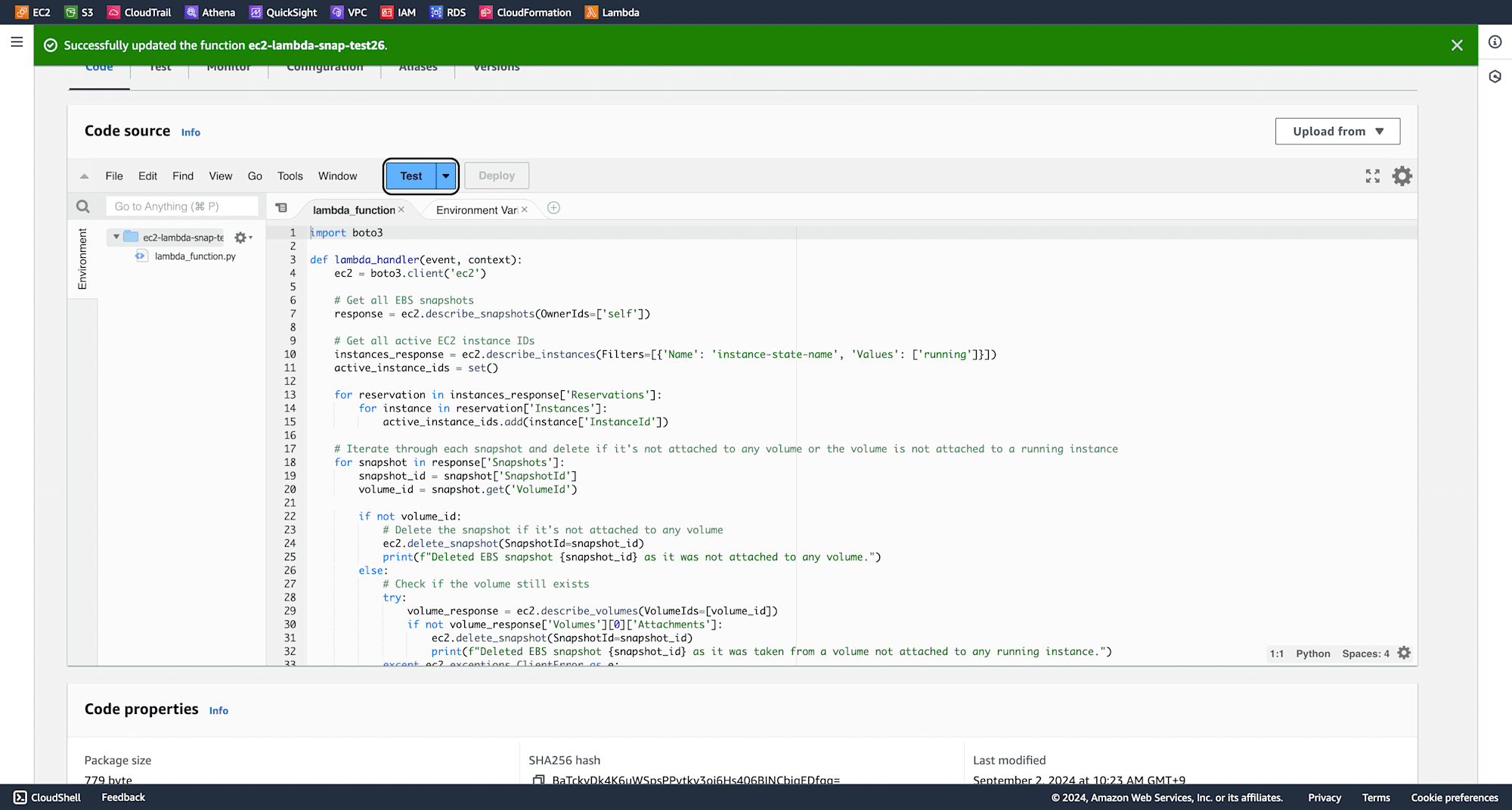
Give an eventname and click on save
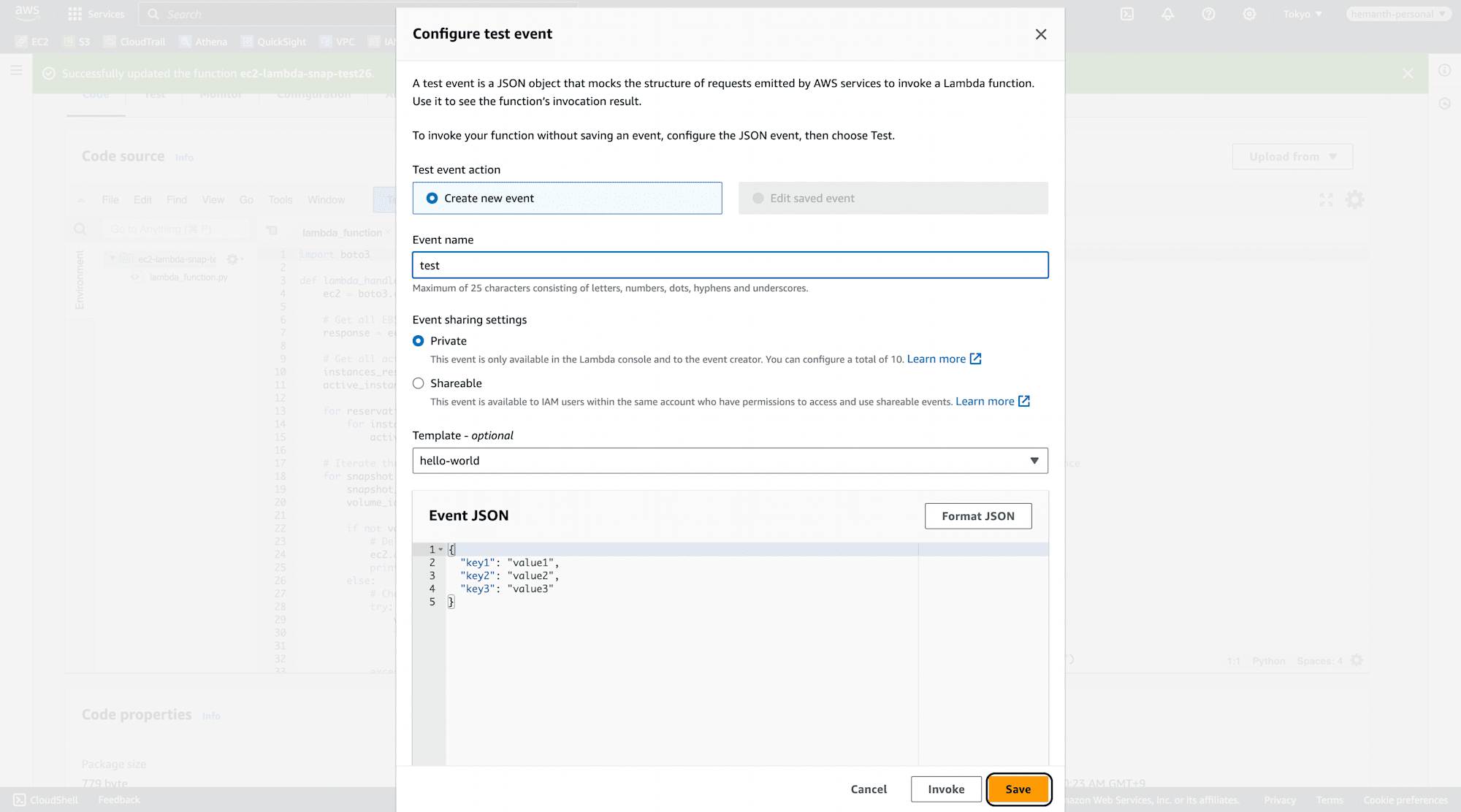
Now click on test and event has run succesfully, since the EC2 instance is still running, the function will not delete any snapshots.
Now, terminate the EC2 instance.
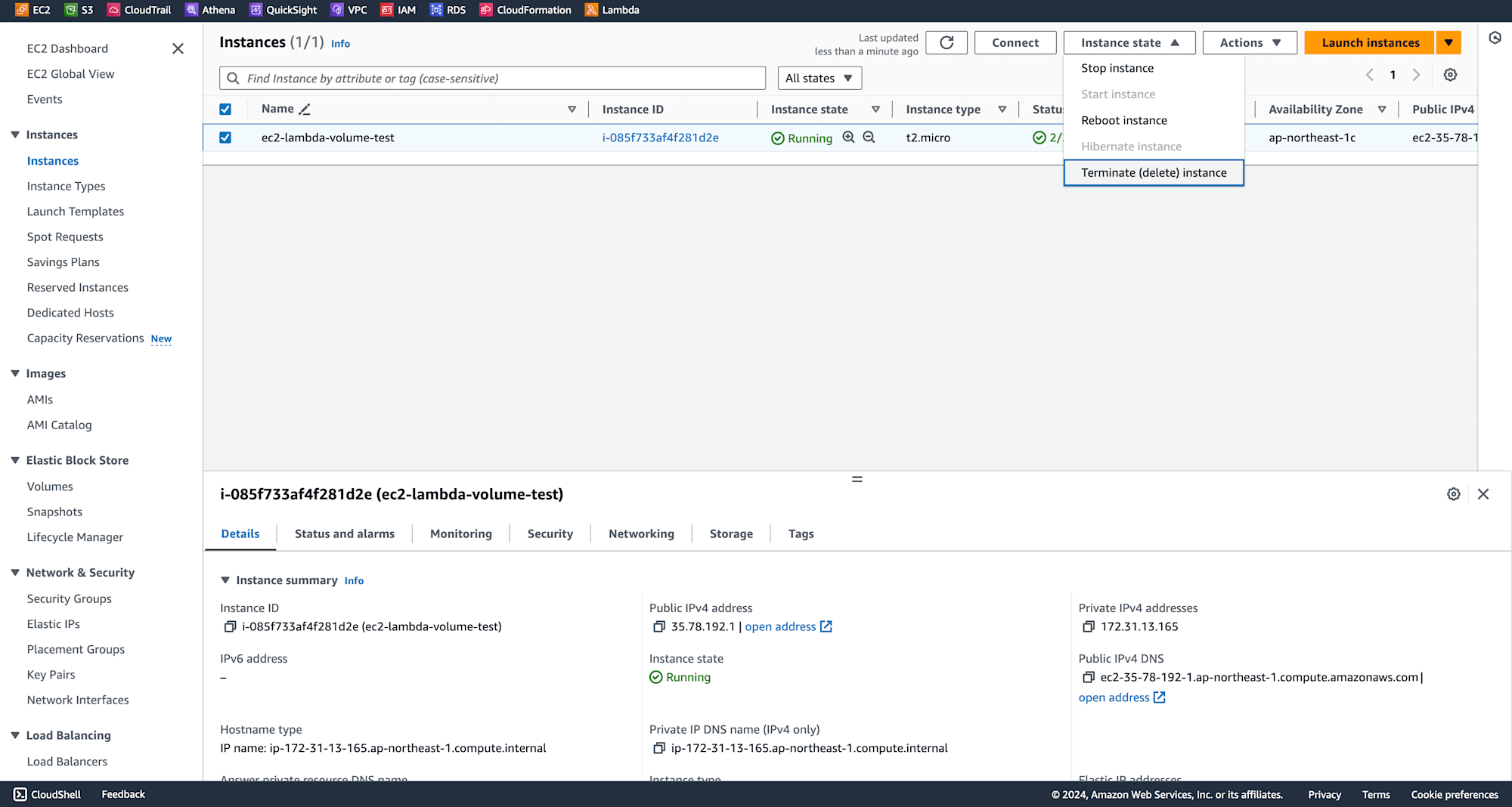
Since EC2 instance is terminated EBS volume associated with it is terminated but not the snapshot
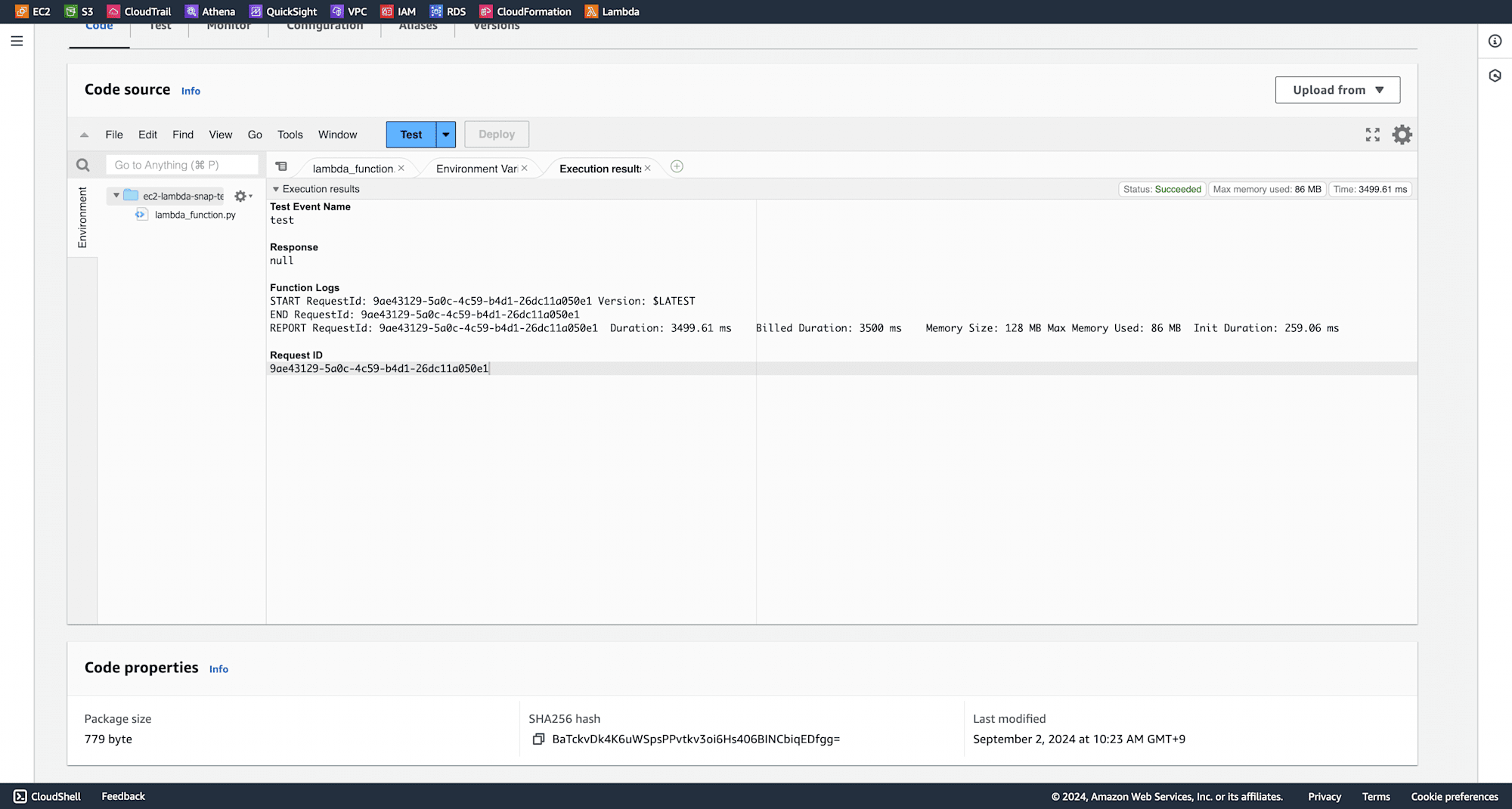
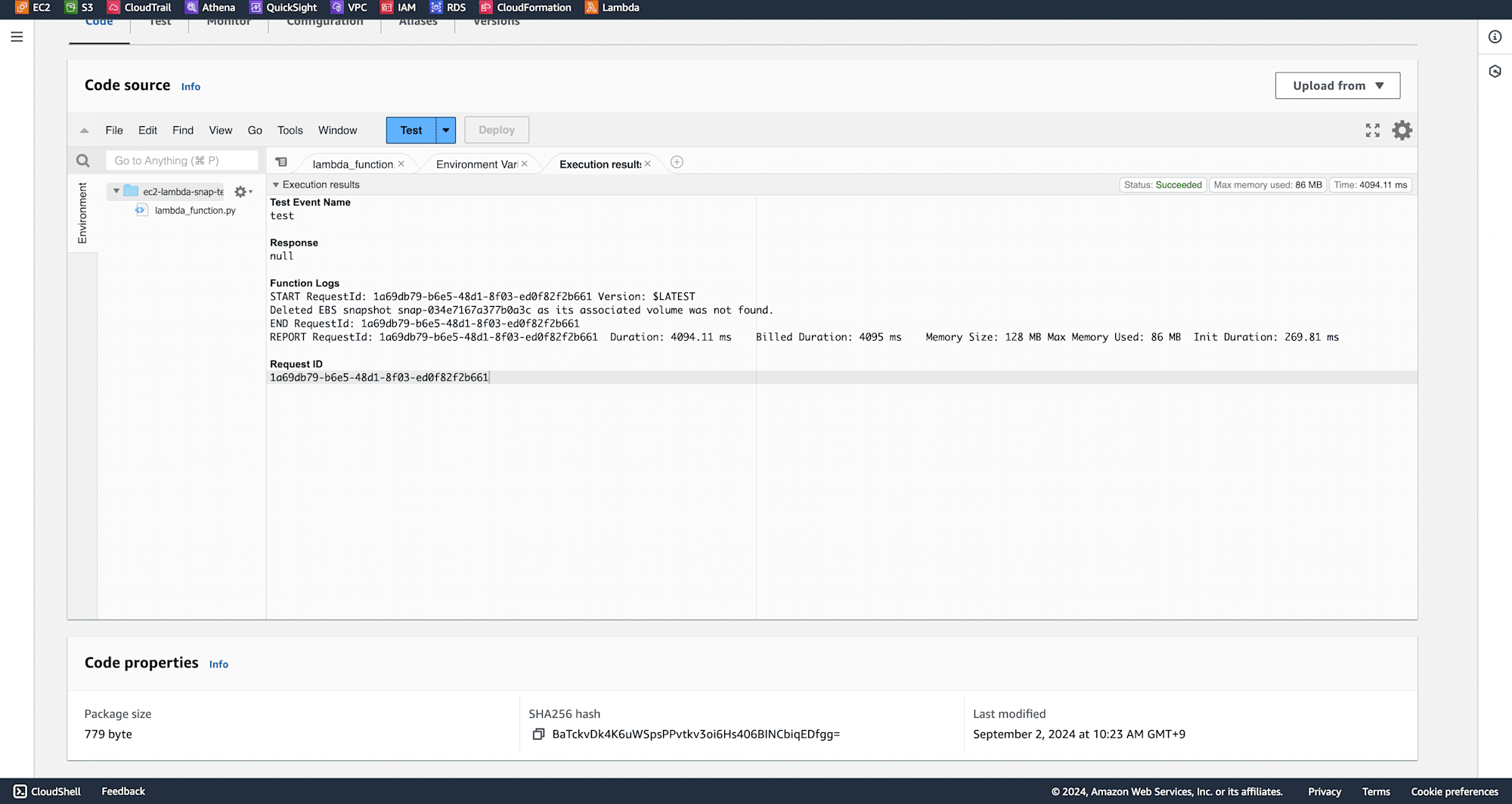
Run the Lambda function again by clicking on Test.
You can observe from function logs that EBS snapshot was deleted
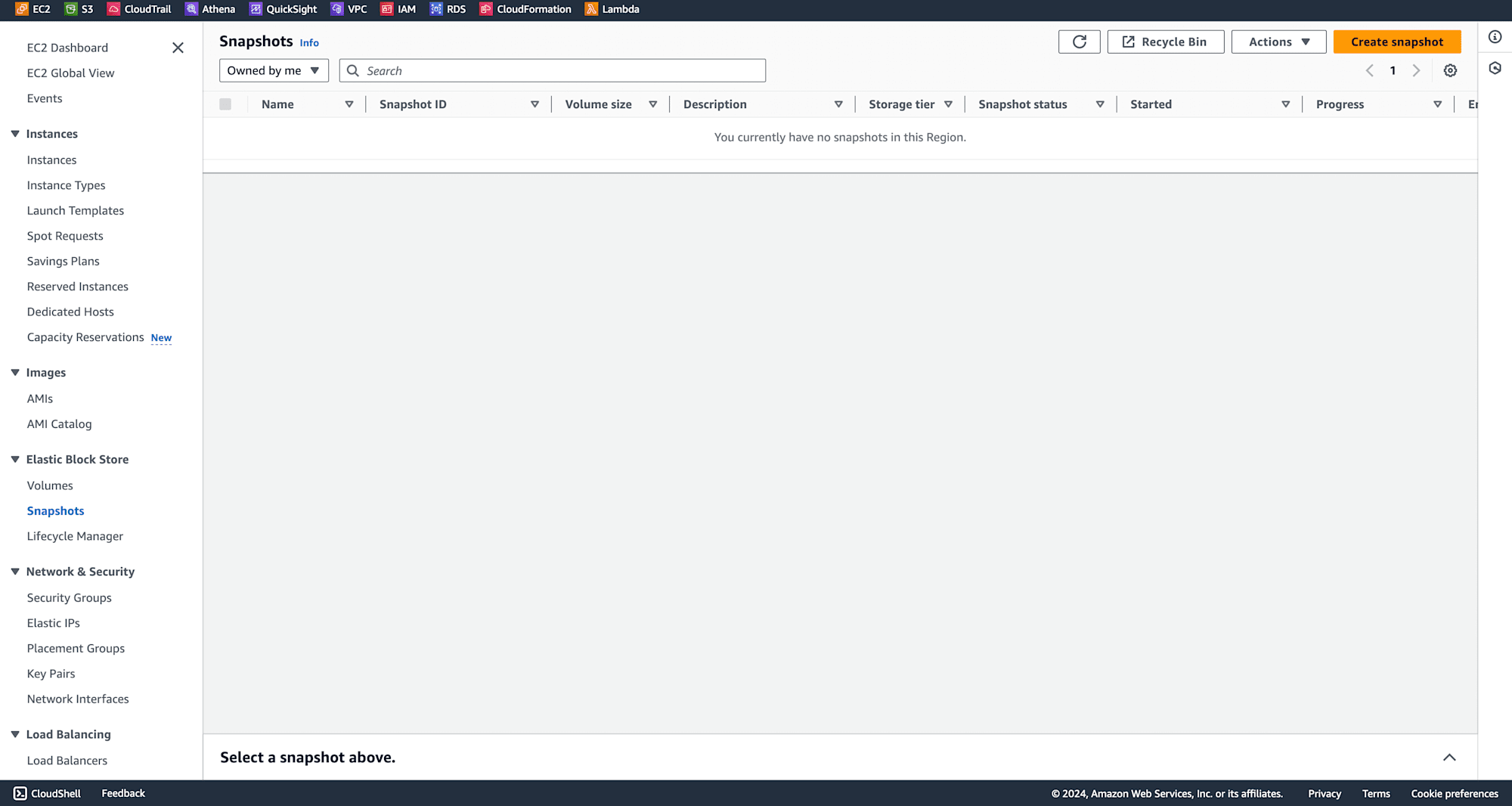
Finally, go back to the Snapshots section to verify that the snapshot has been successfully deleted.
Conclusion
By setting up this Lambda function, we’ve created an automated process to clean up unnecessary EBS snapshots when an EC2 instance is terminated. This not only helps in maintaining a tidy AWS environment but also in reducing storage costs by preventing the accumulation of obsolete snapshots. Implementing such automation can lead to more efficient resource management and significant cost savings in the long run.
